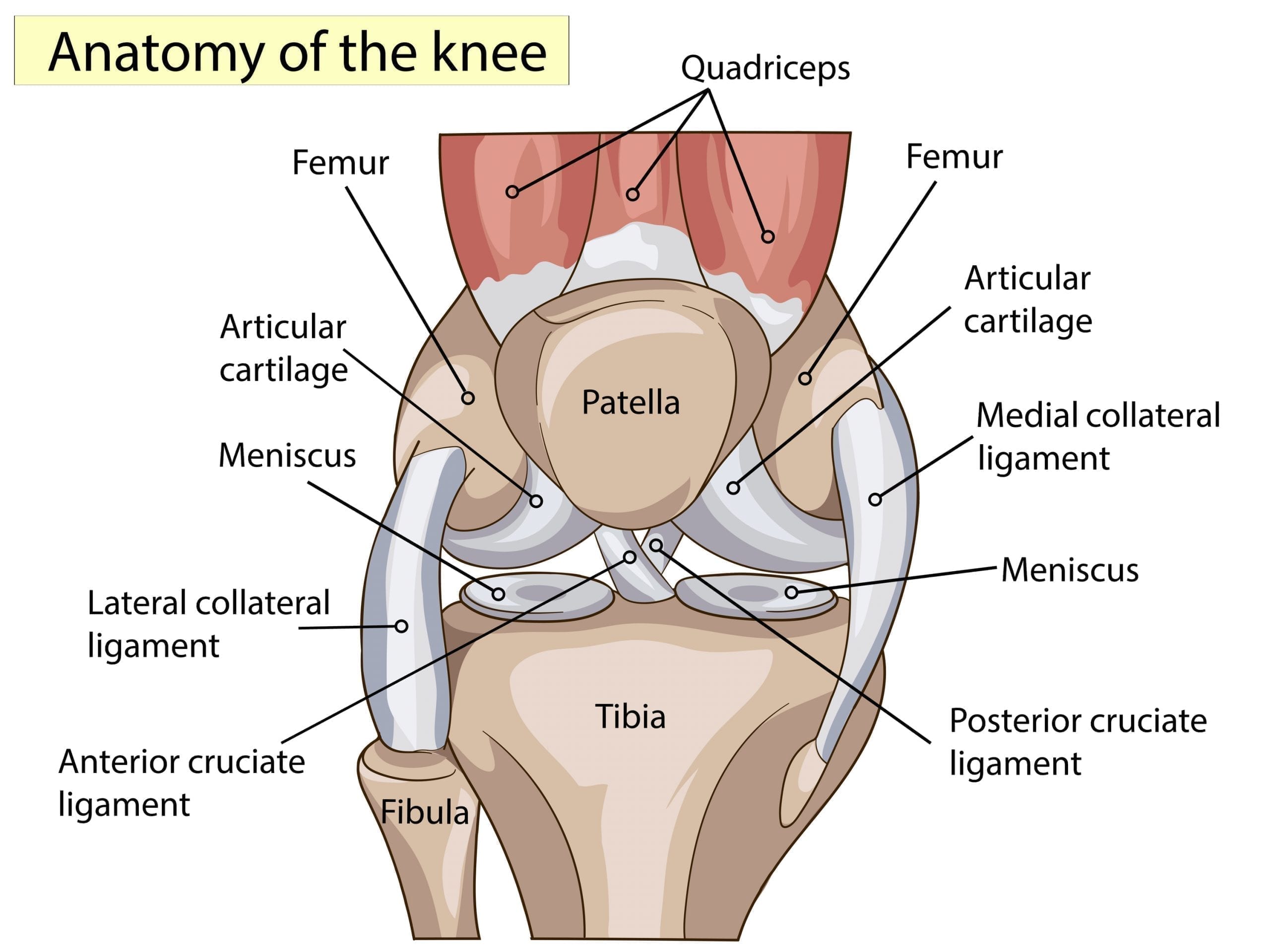
Joints problems can be as a by-result of another injury or caused by inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or more degenerative processes such as Osteoarthritis. These types of condition can be very debilitating as an affected joint is most commonly caused by damaged cartilage tissue, the symptoms being stiffness, swelling and pain.
One of the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis is inflammation in the smaller joints, like the hands or feet, and are frequently mirrored on both sides of the body. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, tenderness and stiffness, often more pronounced in the morning. As the disease progresses, cartilage and bone can also become affected, followed by supporting tendons and ligaments, ultimately weakening the muscle structure in the body. The end result is limited and difficult movement which can feel very debilitating and limiting.
Osteoarthritis mostly affects cartilage in the body. This is the slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint and helps bones move smoothly over each other, absorbing shock of movement. In osteoarthritis, the top layer breaks down and ultimately wears away, causing the bones to rub directly on each other, causing pain, swelling and ultimately loss of motion in the joint. In worst case scenarios, bits of bone or cartilage can break away and float inside the joint space, which can cause much more pain and damage.
How Physiotherapy Helps
Physiotherapy will be part of the treatment solution in addition to other medication likely prescribed by your GP, which could include disease modifying drugs. Physiotherapy exercises will focus on range of motion and strengthening exercises as well as targeting inflammation and swelling reduction. The goal is to restore an easy, pain free movement and will often focus on peripheral areas to the affected joint in order to provide a strong stable platform off which the joint can perform normal function without pain and restriction.
What to expect at your appointment and follow on treatment
- Firstly, we will come to you, take a full medical history, assess your injury and broader body (for related causes) and as your surrounding environment to ensure we have the fullest picture prior to recommending treatment. We will also discuss your expectations which are critical to successful injury rehabilitation.
- For a joint injury, this will include a good look and assessment of your body, which may require you to remove some clothing, so it’s a good idea to dress comfortable and wear suitable underwear.
- We will then form a treatment plan with you, which will include a series of exercises to do outside of our physiotherapy sessions. The most successful recovery happens with your commitment to the plan when the physio isn’t there! And importantly, a bit of patience also… addressing joint problems, particularly if they are chronic, can be a slow progressive rehabilitation, it is important to manage expectations at the outset.
Top Tips for managing joint problems
- Ice or hot water can be your best friends when dealing with a joint.
- Continue with your normal day to day activity as much as possible.
- Don’t overcompensate on your body, which can place undue stress elsewhere.
- Keep moving and continue with activities such as walking or swimming.
- Over the counter pain killers such as ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation but should only be taken on advice by your GP or physio.
- Check your posture when sitting for long periods of time, such as watching TV or playing computer games.
- Avoid sitting for too long in one position, particularly when driving or working (it is advised to have at least a 10minute break every hour, getting up to stretch and move about).
- Gentle stretches can help prevent stiffness.
- Take care when lifting objects, making sure to bend your hips and knees to use the power in your legs (rather than your lower back).
- Check your bed mattress to ensure it supports your body weight properly.
- Look at your general health and diet. Being overweight, or excessive smoking can both impact injury and how quickly your body can recover.